In this article, we draw on our experience as scholars from three different disciplines-economics, law, and political science-to discuss the added value that each of these disciplines brings to the study of fiscal federalism in Canada and to reflect more broadly on how they can complement each other in the context of interdisciplinary collaboration. While disciplinary perspectives can address research questions that stem from specific scholarly traditions, interdisciplinary collaboration allows scholars not only to get a deeper, more holistic picture of policy realities but also to craft and/or assess policy solutions in ways that account for the complexities of the real world.
Daniel Beland, Andre Lecours, Vanessa MacDonnell, Peter Oliver, Trevor Tombe
Canadian Public Policy 50 (S1): 24-35,
2024

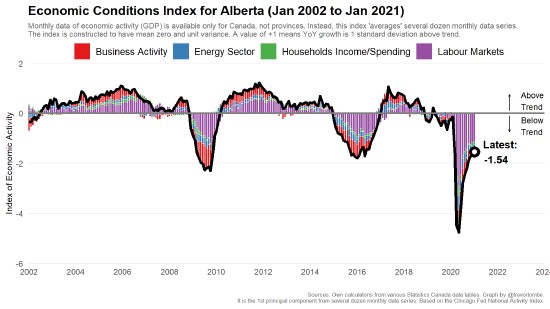
A separate Alberta Pension Plan (APP) has gained renewed attention. This paper assesses the long-run viability of such a plan, using both a detailed quantitative model and simple, intuitive approaches. I find only modest scope for material changes in benefit levels and contribution rates relative to the current Canada Pension Plan (CPP). Specifically, I estimate an APP minimum contribution rate (the rate that maintains predicted plan assets relative to plan expenses) is 8.2 percent, compared to the CPP’s 9.5 percent. I also explore several relevant risks, including future demographic changes and investment risks. I find, for example, that if provincial fertility and migration rates equal the national averages, then approximately 40 percent of Alberta’s pension advantage relative to the CPP is eliminated. Finally, I shed new historical light on a unique area of uncertainty concerning the division of CPP assets. Overall, this paper not only provides an updated foundation to evaluate the potential strengths and weaknesses of an APP but also provides methods to understand public pension sustainability more broadly.
Trevor Tombe
Canadian Public Policy 50 (1): 1-19,
2024
Inflation surged in most advanced economies in 2021 and 2022 before easing considerably in 2023. In Canada, the headline Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 8.1 percent in the year ending June 2022, then declined to 2.8 percent by June 2023 - the most pronounced acceleration and deceleration in the pace of price changes in decades. Canada’s inflation experience is not unique: in the United States, consumer price growth peaked at 9.1 percent in June 2022, while the Euro Area peaked at 10.6 percent in October 2022. In this paper, we examine several key drivers of Canada’s recent decline in inflation. In particular, we measure product-level price changes and identify whether they are mainly supply-driven (i.e., energy prices, wages, or other input costs) or demand-driven (i.e., consumer expenditures, fiscal policy, and so on). We find most of the decline can be attributed to the falling price of energy, a product directly purchased by households and an input in the production of nearly all goods and services. Both supply- and demand-side factors have played a role, with a substantial reduction in demand-driven factors accounting for most of the overall fall in the pace of consumer price growth. Today, a greater portion of the remaining price pressures stem from supply-side factors, especially in housing and groceries. It may be necessary for the Bank of Canada to continue implementing a robust tightening of monetary policy to counteract the price pressure from the supply side.
Yu Chen, Trevor Tombe
C.D. Howe E-Brief,
2023
We study how goods- and labor-market frictions affect aggregate labor productivity in China. Combining unique data with a general equilibrium model of internal and international trade, and migration across regions and sectors, we quantify the magnitude and consequences of trade and migration costs. The costs were high in 2000, but declined afterward. The decline accounts for 36% of the aggregate labor productivity growth between 2000 and 2005. Reductions in internal trade and migration costs are more important than reductions in external trade costs. Despite the decline, migration costs are still high and potential gains from further reform are large.
Trevor Tombe, Xiaodong Zhu
American Economic Review,
2019